The Core
The MGH NGS core is associated with the Department of Molecular Biology. The core currently operates two NextSEq 2000 sequencers and a MiSeq. The core owns a 10X Chromium X, Luna FX7 fluorescent cell counter, Tapestation 4200, and BioRad CFX384 qPCR. The core has access to shared instruments for DNA shearing, etc.
Current members of the core:
Ulandt Kim ukim@molbio.mgh.harvard.edu
Stephanie Valencia
General inquiries sequencing@molbio.mgh.harvard.edu
Director:
Ruslan Sadreyev
Sequencing library construction and QC
Before sequencing, your DNA or RNA will need to be fragmented and have Illumina-specific adapters added. The adapters facilitate binding to the flowcell surface and contain priming sites and barcodes. The pool of adapter-ligated barcoded fragments is called a “library”. The core specializes in 10X single-cell library construction, but will accept completed Illumina libraries of other types (RNA-seq, DNA-seq, etc.) for library QC and sequencing. The core will not be accepting new submissions for bulk-input DNA/RNA library construction. If you have an ongoing project with the core, please contact us.
For 10X single-cell library construction cells can be submitted in the following forms: fresh, frozen, dissociated from FFPE blocks, or formaldehyde-fixed.
Library QC consists of Tapestation followed by qPCR. This service also includes library pooling.
Sequencing settings
The NextSeq 2000 system can run Illumina’s latest XLEAP chemistry that continues the trend towards lower sequencing costs. Illumina has added different kit options for the NextSeq 2000. At present there are kits of four different outputs (total reads/clusters), designated P1 through P4. There are also different numbers of cycles/bases available. This table lists all options:
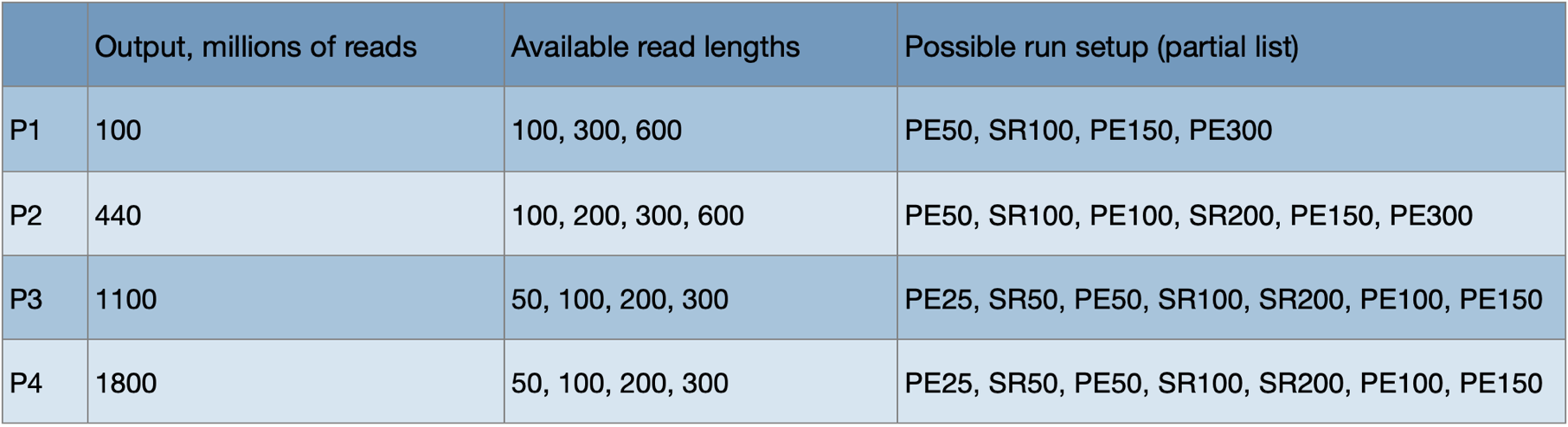
Kits can be run in either single-read (SR) or paired-end (PE) mode. For example, a 200 cycle kit can be used for SR200 or PE100. Extra cycles are included for index read(s). Cost per read/base is lower with larger kits and longer runs. In order to operate economically, the core will not sequence until the full capacity of the kit is reached.
Note that 10X libraries require an unusual run setup (PE 28/90), but it is equivalent to PE50 in price.
Turnaround considerations
Shared vs independent runs:
If your sequencing needs align with the output of one of the kit types, P1-P4, then you can sequence on a run of your own. If your needs fall in between the outputs of the kit types, or if you would like to sequence a small project on a more cost-effective larger flowcell, then the core can pool your samples with others on a shared run. The advantage of an independent run is potentially faster turnaround since you would not have to wait for other submissions to fill the run to capacity. The advantage of a shared run is flexibility to choose any output you need, and potentially lower cost.
Run type vs run time examples:
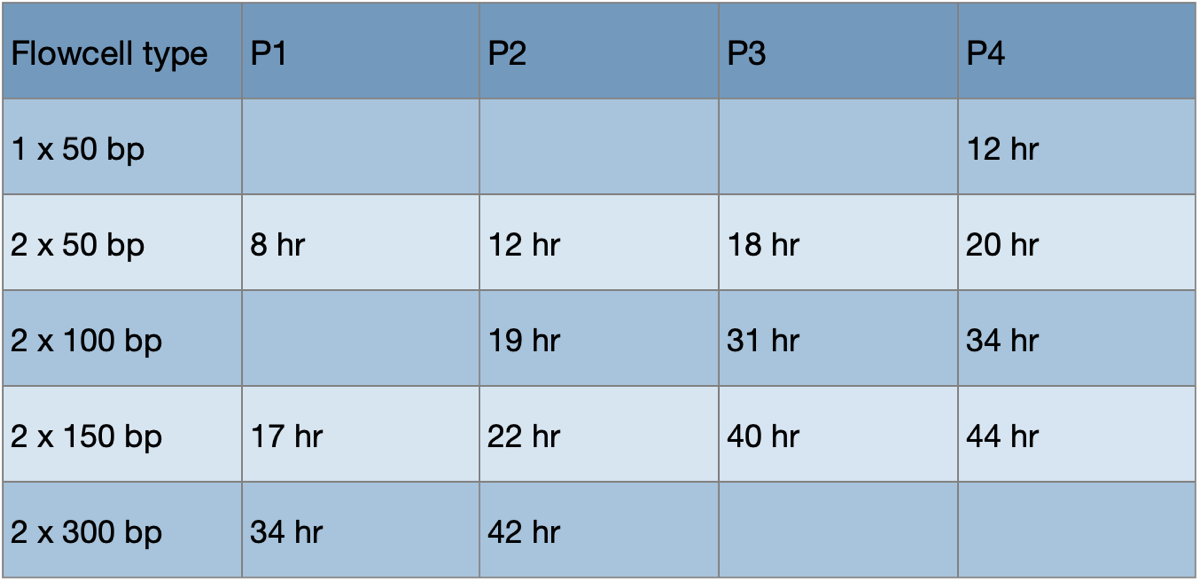
Avoiding conflict:
Data from shared flowcells is demultiplexed with barcodes/indexes that are sequenced along with the data. Every sample’s barcode must be unique. If you are making your own libraries and sequencing on a shared flowcell, feel free to contact the core before you choose your barcodes.
Custom primers:
The core cannot use custom sequencing primers on shared flowcells. If you have a custom sequencing primer, please plan your project around the output of one of the kits, P1-P4 or MiSeq.
Bioinformatic analysis
If you need analysis, the NGS Core is attached to the Bioinformatics core. Analysis is a consultancy-based service at an hourly rate. Contact our director, Ruslan Sadreyev, at sequencing@molbio.mgh.harvard.edu
Data policy
Data files should be downloaded and saved to a safe location – or preferably two. Old files on the core’s servers will be purged when space is needed. Please do not rely on the core as a backup. This applies to both raw and analyzed data.
You may also want to pick up your finished samples and/or libraries. These will be saved for a minimum of 6 months, after which they will be discarded as the freezers fill up.
